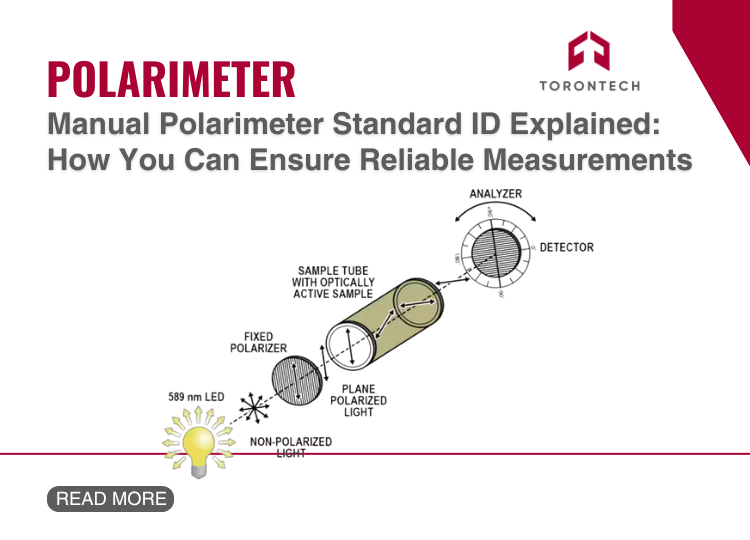
When working with a manual polarimeter, achieving reliable and accurate measurements isn’t just about using the right equipment. It’s also about ensuring proper calibration. One critical component of this process is understanding and applying the manual polarimeter standard ID.
This unique identifier, tied to specific calibration standards, ensures traceability, data integrity, and quality control in polarimetric analysis. Let’s break it down and show you how to use this effectively in your lab.
What Is a Manual Polarimeter Standard ID?

A manual polarimeter standard ID is more than just a label. It’s a unique identifier assigned to calibration standards such as quartz control plates, sucrose solutions, or other optically active compounds.
This ID provides important details, such as the source, specifications, and usage history, ensuring that every measurement you take is accurate and reliable.
Here’s how it works for you:
1. Traceability
The standard ID enables you to track the origin and history of the calibration material. This traceability ensures that the standard is authentic and reliable, minimizing the risk of errors from unknown or compromised sources.
2. Calibration Verification
Standards with known optical rotation values provide a benchmark for verifying and calibrating your polarimeter’s accuracy.
3. Data Integrity
Accurate documentation of standard IDs ensures that all measurements and calibrations are traceable, promoting data reliability and regulatory compliance.
4. Quality Control
The standard ID acts as a reference point, helping you identify potential instrument issues or measurement errors, enhancing overall quality control processes.
Types of Standards and Their IDs
You’ve likely worked with several types of calibration materials. Each type comes with a unique standard ID that provides critical information about its properties and origin:
1. Quartz Control Plates
These are highly precise plates made of quartz crystal, known for their stable and consistent optical rotation values. Their standard IDs typically include the manufacturer, lot number, and specific rotation value. Quartz plates are excellent for long-term use because of their durability and reliability.
2. Sugar Solutions
Common in many labs, sucrose solutions with known concentrations are a popular calibration choice. Their IDs often include details about the sugar type, concentration, and preparation date, ensuring traceability for each use.
3. Other Chiral Compounds
Solutions of optically active compounds, such as tartaric acid or amino acids, can also be used as standards. Their standard IDs provide information about the compound name, concentration, and other relevant specifications.
By using these standards, you create a reliable foundation for your polarimetric measurements.
Why Do Standard IDs Matter?

Standard IDs might seem like a minor detail, but they have a significant impact on your work. Here’s why they matter to you:
1. Keep Your Results Consistent
Without traceable standards, even slight variations can compromise your results. Using standard IDs ensures your data stays consistent, no matter how often you measure.
2. Ensure Accurate Measurements
Calibration with standards featuring known optical rotation values helps you maintain the highest level of accuracy. This is especially important when precise results are critical, such as in pharmaceuticals or food quality control.
3. Simplify Record-Keeping
Keeping track of standard IDs streamlines your documentation, saving you time and helping you meet regulatory requirements.
Important Things You Must Know
To fully utilize manual polarimeter standard IDs and maintain reliable measurements, understanding broader guidelines and best practices is essential. Here’s what you must know:
1. Instrument-Specific Manuals Are Your First Resource
Every polarimeter model is unique, and its operation manual is your go-to guide. These documents often include sections on calibration, proper use of standards, and the importance of recording standard IDs. Make sure you familiarize yourself with these details, as they are tailored specifically to your equipment.
2. Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) Cover Standard Use
General GLP guidelines emphasize traceability and proper record-keeping, even if they don’t explicitly mention “standard IDs.” They provide foundational principles for using and documenting calibration standards effectively.
Look for GLP guidelines from organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or your industry’s regulatory body. Following these practices ensures your measurements meet industry standards and regulatory requirements.
By integrating these practices, you align your processes with global standards and maximize the reliability of your polarimetric measurements.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and using the manual polarimeter standard ID isn’t just about meeting industry standards. It’s about improving the quality and reliability of your work. By selecting the right standards, calibrating carefully, and maintaining proper records, you ensure that every measurement you take is accurate and trustworthy.
This attention to detail not only enhances your results but also builds your confidence in the data you produce. Take the time to implement these practices, and you’ll see the difference they make in your polarimetric analysis. Accurate measurements start with informed choices and now, you have the tools to make them.