When it comes to precise color measurement and analysis, the debate of colorimeter vs spectrophotometer often comes up. If you’ve ever found yourself wondering “What is a colorimeter?” or “What is the difference between a colorimeter and a spectrophotometer?”, you’re in the right place.
In this article, we break down the differences, applications, and how to choose the right tool for your needs.
What is a Colorimeter?
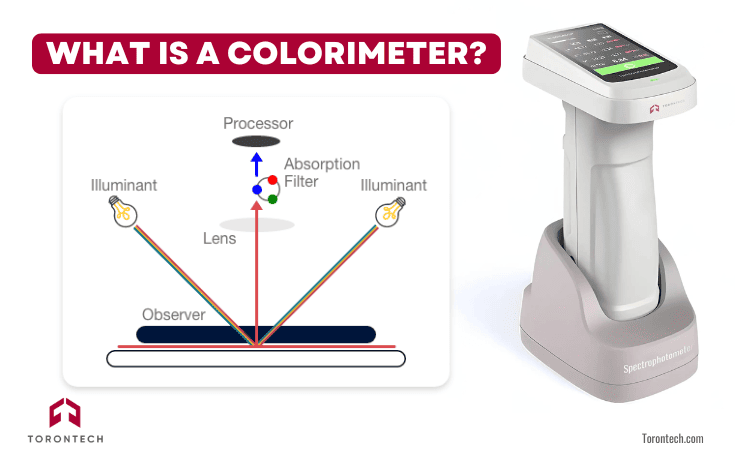
A colorimeter is kind of like a translator between your eyes and science. It mimics how humans perceive color, using three filters—red, green, and blue—to break down what it sees. This process gives us something called “tristimulus values,” which is just a fancy way of saying: it turns color into numbers.
You might also hear it referred to by another name: a color photometer. So, if you’re asking “What is another name for a colorimeter?”, there you have it.
These devices are commonly used in colorimeter chemistry, for concentration testing, comparing the color of materials, or for basic color quality checks across production environments.
You’ll find handheld colorimeters used by designers on the go, portable colorimeters in the field, and benchtop colorimeters in labs where precision matters. And if you’re dealing with standardized testing, an ASTM colorimeter ensures everything’s up to industry code.
Components of a Colorimeter
- Illuminant: Provides a fixed light source (e.g., daylight or incandescent).
- Observer: Simulates a 2° field of view, like how the human eye sees.
- Tristimulus filters: Separate incoming light into RGB components.
This makes colorimeters ideal for assessing color differences, strength, and fastness.
Types of Colorimeters
- Handheld colorimeter / portable colorimeter: Perfect for fieldwork or on-site testing.
- Benchtop colorimeter: Best suited for lab environments requiring repeatable measurements.
- ASTM colorimeter: Instruments that adhere to ASTM standards for consistency and traceability.
How Does a Colorimeter Work?
Colorimeter operates by passing a beam of light through a solution and measuring the amount of light absorbed. The more concentrated the solution, the more light is absorbed. This absorbance is then translated into a concentration value using the Beer-Lambert law.
If you’re wondering “How do you use a colorimeter?” or “How to use a colorimeter?”, the process is straightforward:
- Turn it on and calibrate it (usually with a blank sample).
- Place your sample.
- Select your settings (like wavelength).
- Hit “measure” and let the magic happen.
It’s fast, user-friendly, and perfect for routine tasks.
Colorimeters: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Easy to use and fast results
- Portable and cost-effective
- Focuses on human-relevant color differences
Cons:
- Limited to RGB data, not full spectral
- Cannot detect metamerism (when two colors look the same under one light but not another)
- Not ideal for colorant formulation or R&D
What is a Spectrophotometer?
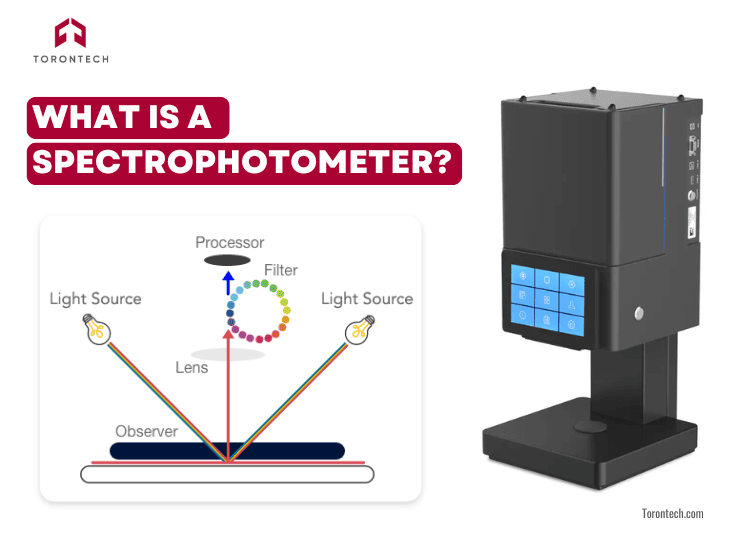
While a colorimeter measures color based on how we see it, a spectrophotometer goes several steps further. It measures light intensity across the full visible spectrum (and often beyond), providing a detailed breakdown of how a material absorbs, reflects, or transmits light at each wavelength.
In short, if you need deeper insight, a spectrophotometer delivers.
It’s commonly used for color formulation, identifying metamerism, or measuring optical properties like haze and turbidity, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, paints, plastics, and food.
Components of a Spectrophotometer
- Adjustable Illuminant: Can simulate various light sources, including UV and fluorescent.
- Observer: Often set at a 10° standard, better suited for industrial applications.
- Grating or Prism System: Splits light into individual wavelengths for detailed analysis.
Types of Spectrophotometers
- UV-VIS and VIS models
- Atomic absorption spectrophotometers
- Infrared spectrophotometers
- Fluorescence spectrophotometers
- Portable and benchtop color spectrophotometer
How Does a Spectrophotometer Work?
Here’s how it works:
- A light source emits a beam across a range of wavelengths.
- The beam is split by a prism or diffraction grating.
- Each wavelength interacts with the sample individually.
- A detector measures absorbance, reflectance, or transmittance.
- The software or processor interprets the data into visual and numeric outputs.
This level of detail allows you to monitor both color and turbidity in a single measurement, ideal for transparent liquids or substances where clarity matters just as much as color.
Spectrophotometers: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Offers full spectral data
- Can detect metamerism and colorant strength
- Highly versatile across sample types and lighting conditions
- Suitable for precise color formulation and quality control
Cons:
- More expensive
- Slightly more complex to operate
- May be overkill for simple color comparisons
Colorimeter vs Spectrophotometer: Key Differences
So, what is the difference between a colorimeter and a spectrophotometer? Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Colorimeter | Spectrophotometer |
| Measurement Type | Tristimulus (RGB) | Spectral (wavelength-by-wavelength) |
| Light Range | Fixed or limited wavelengths | Full visible spectrum (and often UV/IR) |
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Portability | High | Varies (portable or benchtop) |
| Metamerism Detection | No | Yes |
| Complexity | Simple operation | More complex setup |
| Applications | Basic QC, color comparison | R&D, color formulation, full-spectrum analysis |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
While colorimeters are ideal for quick and routine tests, spectrophotometers are better for research, development, and when dealing with complex or highly precise requirements.
Applications of Colorimeter and Spectrophotometer
Understanding the application of colorimeter and spectrophotometer can help you decide which one is better suited for your needs.
Applications of Colorimeter
- Water and wastewater analysis
- Food and beverage quality control
- Soil and fertilizer testing
- Textile and dye industries
- Clinical diagnostics
In fact, organizations often use an ASTM colorimeter to ensure compliance with standard color measurement protocols. You can also find them in different formats, including benchtop colorimeters for lab use and portable colorimeters or handheld colorimeters for field testing.
Applications of Spectrophotometer
- Pharmaceutical analysis
- Paint and coatings color matching
- Forensic and biochemical analysis
- UV/Vis absorbance studies
- Quality control in plastics and polymers
Choosing the Right Tool for You
Now that you understand the difference between spectrophotometer vs colorimeter, how do you choose the right one?
Choose a colorimeter if you:
- Perform high-throughput, routine measurements
- Need a budget-friendly and portable solution
- Don’t require metamerism detection or spectral data
- Want something easy to operate on the shop floor
Go for a spectrophotometer if you:
- Need precise, spectral data for research or formulation
- Work with visually complex or textured materials
- Require flexibility with light sources or observer angles
- Want to detect subtle color differences across environments
Final Thoughts
When it comes to colorimeter vs spectrophotometer, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It really comes down to what you need the device to do, how much precision you require, and the environment in which you’ll be working.
If you’re measuring basic color differences in a production environment, a colorimeter may be exactly what you need. If you’re working on product development, color matching, or quality control across multiple lighting conditions, a spectrophotometer will offer the depth and accuracy required.
Still weighing your options on colorimeter vs spectrophotometer? Remember: simplicity versus precision. Tristimulus versus spectral. Perception versus performance.
Whichever path you choose, you’re taking a critical step toward building a reliable, repeatable, and data-driven approach to color quality.
Explore Torontech’s Advanced Color Measurement Solutions
Now that you have a clear understanding of colorimeters vs. spectrophotometers, you might be wondering where to begin when it comes to choosing a reliable, high-performance instrument. That’s where we come in.
At Torontech, we’ve developed a comprehensive range of color measurement solutions, designed with precision, ease of use, and real-world industry needs in mind. Whether you’re looking for a compact tool for routine checks or a sophisticated instrument for advanced color analysis, we’ve got you covered.
Here’s a look at some of the standout options in our portfolio:
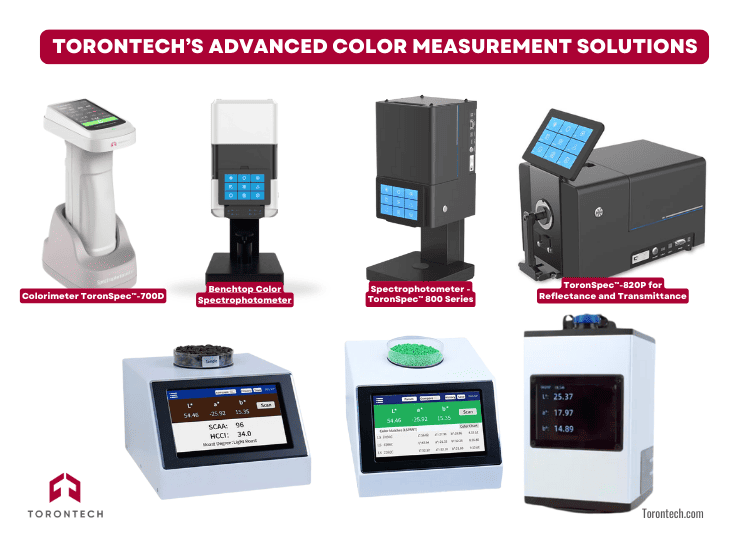
- ToronSpec™ 700D – Portable Color Spectrophotometer & Colorimeter: A portable, dual-function device offering both colorimeter and spectrophotometer capabilities in one compact, on-the-go solution. Ideal for quick, high-accuracy spot checks in the field or on the production line.
- Benchtop Color Spectrophotometer & Colorimeter: Designed for laboratory environments, this benchtop model delivers dependable performance for consistent color quality control and comparative analysis.
- High-Precision Benchtop Color Spectrophotometer: Engineered for demanding R&D applications, this high-precision model provides full-spectrum analysis, enhanced software capabilities, and multi-geometry measurements.
- ToronSpec™ 820P – Benchtop Spectrophotometer for Reflectance & Transmittance: A versatile spectrophotometer capable of both reflectance and transmittance measurements—perfect for analyzing solid, transparent, or liquid samples.
- ToronSpec™ LA – Large Aperture Colorimeter: Specifically designed to measure color over large or uneven surfaces. An excellent choice for textiles, packaging, and other materials requiring a broader measurement field.
- CaffeSpectra – Coffee Spectrophotometer & Colorimeter: Tailored for the beverage industry, CaffeSpectra ensures accurate analysis of roast levels and color consistency in coffee production—because color isn’t just aesthetic, it’s part of the flavor profile.
- Non-Contact Color Spectrophotometer & Online Color Sensor: Ideal for inline and real-time quality control. This non-contact system integrates seamlessly into your production process, enabling immediate feedback and minimizing downtime.
Need Help Choosing the Right Solution?
Whether you’re just starting to build your color quality control process or upgrading your current system, our experts at Torontech are here to help. We’ll work with you to understand your goals, recommend the right equipment, and ensure you get the best value from your investment.
Explore our full range at our site or contact us today to schedule a consultation.