The twin screw extruder is a versatile and widely used piece of equipment in the manufacturing industry, particularly in the processing of polymers, plastics, and other materials. This powerful machine plays a crucial role in transforming raw materials into a wide range of products, from plastic packaging to advanced composite components.
But what exactly is a twin screw extruder machine? How does it work? And what are its applications? In this blog post, we’ll explore the inner workings of the twin screw extruder, delving into its key elements, operational principles, and the diverse applications that leverage its capabilities.
What is Twin Screw Extruder Machine?
A twin screw extruder machine is a specialized equipment designed to process and extrude various materials, particularly polymers and plastics. Unlike its single-screw counterpart, the twin screw extruder features two parallel screws that rotate in the same direction within a heated barrel. This unique configuration offers several advantages, making it a popular choice for manufacturing applications.
The twin screw extruder’s design allows for efficient mixing, kneading, and homogenization of the material being processed. As the twin screws rotate, they create a self-wiping action that prevents material buildup on the barrel walls, ensuring consistent and uniform extrusion. This feature is particularly beneficial when working with viscous materials like molten plastics or rubbers.
The Significance of Twin Screw Extruders in Plastic Processing
When processing plastics, the twin screw extruder machine plays a vital role in melting, mixing, and shaping the material into the desired form. The screws’ intermeshing action generates shear forces that help break down the plastic pellets or granules, ensuring thorough melting and dispersion of additives or fillers. This results in a homogeneous melt that can be extruded through a die to produce various products, such as pipes, sheets, or profiles.
One of the most common applications of the twin screw extruder plastic is in the production of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) products. PVC twin screw extruders are designed to handle the unique properties of this versatile material, providing precise temperature control and efficient mixing to ensure consistent quality.
Understanding the Difference between Single Screw and Twin Screw Extruders
Compared to single screw extruders, twin screw extruders offer several advantages. They are known for their superior mixing capabilities, which is essential for achieving uniform dispersion of additives or fillers. Additionally, twin screw extruders can process a wider range of materials, including highly viscous or abrasive compounds, making them more versatile for various applications.
The difference between single screw and twin screw extruders lies in their design and operational principles. Single-screw extruders rely on a single rotating screw to convey and melt the material, while twin-screw extruders utilize two intermeshing screws that provide better mixing and shearing action. Twin screw extruders also offer better control over residence time and temperature, enabling more precise processing of sensitive materials.
Twin Screw Extruder Elements
The twin screw extruder machine is a complex piece of equipment with several key components that contribute to its efficient operation and performance. One of the most crucial elements is the screws themselves, which come in various types and configurations.
1. Screws
- Co-rotating Screw: In this design, both screws rotate in the same direction, suitable for applications that require high mixing and kneading action.
- Counter-rotating Screws: Some twin screw extruders feature screws that rotate in opposite directions, providing unique mixing and shearing capabilities for specific applications especially those that require high compression and shear forces..
- Intermeshing Screws: The screws in a twin screw extruder are designed to intermesh with each other, allowing for optimal material conveyance, melting, and mixing. The intermeshing action creates high shear forces, which contribute to thorough homogenization and dispersion of additives or fillers.
2. Barrel
The screws are encased within a heated barrel, which provides the necessary temperature control for melting and processing the material. The barrel is typically divided into multiple zones, each with independent temperature control, allowing for precise management of the temperature profile along the extrusion path.
3. Feed Zone
This zone is where the raw material, typically in the form of pellets, granules, or powder, is introduced into the extruder. Its design ensures smooth and consistent feeding of the material onto the screws.
4. Melting and Conveying Zones
As the material moves along the screws, it encounters these zones, where the combination of heat from the barrel and shear forces from the screws gradually melts and plasticizes the material.
5. Kneading and Mixing Zones
These zones feature specific screw elements, such as kneading blocks or mixing sections, that provide intensive mixing and shearing action, ensuring thorough homogenization of the melt.
6. Venting and Vacuum Zones
Twin screw extruders often incorporate venting or vacuum zones, which allow for the removal of volatile components or air from the material, improving the overall quality and consistency of the extruded product.
7. Die
The die is the final component, where the molten and homogenized material is forced through a shaped orifice to form the desired product shape.
By understanding the functions and interactions of these key elements, including the various types of screws and their configurations, manufacturers can optimize the twin screw extruder’s performance and achieve consistent, high-quality extrusion results for a wide range of materials and applications.
How Does a Twin Screw Extruder Work?
The working principle of a twin screw extruder machine is based on its unique design, featuring two parallel screws that rotate in opposite directions within a heated barrel. This configuration plays a crucial role in efficiently processing and extruding various materials, especially plastics. Let’s discuss how the twin screw extruder works step by step.
1. Material Feeding
The extrusion process begins by introducing the raw material, typically plastic pellets, granules, or powder, into the barrel through a hopper. This ensures a consistent and controlled flow of the material onto the counter-rotating screws.
2. Conveying and Compression
As the twin screws rotate in opposite directions, they convey the raw material towards the end of the barrel. During this process, the screws’ intermeshing design compresses and kneads the material, generating heat through shear forces and friction.
3. Plasticization and Melting
As the material progresses along the screws, the combination of heat from the heated barrel and the compression and shearing action gradually melts and plasticizes the raw material, converting it into a homogeneous molten mixture.
4. Intensive Mixing and Homogenization
The counter-rotating screws provide a high degree of mixing and kneading action, which enhances the plasticization and homogenization of the molten plastic material. This step ensures thorough mixing and dispersion of additives, fillers, or reinforcements, resulting in a consistent and uniform melt.
5. Melt Pumping and Die Formation
Once the material is fully melted and homogenized, the screws continue to convey and pump the molten plastic mixture towards the end of the barrel, where it is forced through a carefully designed die. The die shapes the molten material into the desired form, such as pipes, sheets, profiles, or other customized shapes.
6. Cooling and Calibration
As the extruded plastic product emerges from the die, it may undergo further cooling and calibration processes, depending on the specific application and product requirements. This could involve water baths, air cooling systems, or sizing equipment to ensure consistent dimensions and properties.
The twin screw extruder machine’s unique design, with counter-rotating screws and intensive mixing capabilities, makes it highly efficient for processing and extruding a wide range of plastic materials. The self-wiping action of the intermeshing screws and the ability to handle different viscosities contribute to the machine’s versatility in various industrial applications involving plastic extrusion.
Advantages of Twin Screw Extruder
Twin screw extruders offer several distinct advantages over their single-screw counterparts, making them a preferred choice for various extrusion applications. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of twin screw extruders provide.
- Superior Mixing and Homogenization: capabilities due to the intermeshing, counter-rotating screws generating high shear forces, ensuring uniform dispersion of additives and fillers.
- High Output Rates and Throughput: enabled by the efficient design and self-wiping action of the screws, allowing for continuous processing and increased production efficiency.
- Versatility in Material Processing: capable of handling a wide range of materials, from highly viscous polymers to low-viscosity fluids, including abrasive or filled compounds.
- Precise Temperature Control: with multiple heating and cooling zones along the barrel, crucial for processing temperature-sensitive materials or achieving specific product properties.
- Improved Melt Quality: with a homogeneous and consistent melt, free from thermal degradation or localized overheating, contributing to better product quality.
- Reduced Residence Time: due to continuous material flow and efficient conveying, beneficial for heat-sensitive materials or minimizing degradation.
- Modular Design: allowing for easy reconfiguration or replacement of screw elements, enabling adaptability to different processing requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: often requiring less energy for material processing compared to single-screw extruders, leading to cost-effectiveness and reduced environmental impact.
These advantages make twin screw extruders a versatile and efficient choice across various industries, including plastics, rubber, food, and pharmaceuticals.
Types of Twin Screw Extruders
While twin screw extruders share many common features and principles, there are different types designed to cater to specific applications and requirements. Two main categories of twin screw extruders are widely used in various industries:
1. Parallel Twin Screw Extruder
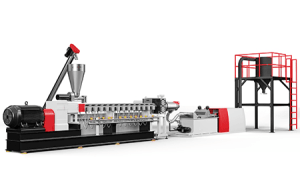
- This type of twin-screw extruder features two parallel screws that rotate in the same direction, either co-rotating or counter-rotating.
- Co-rotating screws rotate in the same direction, while counter-rotating screws rotate in opposite directions.
- Parallel twin screw extruders are known for their excellent mixing and homogenization capabilities, making them suitable for applications requiring uniform dispersion of additives or fillers.
- They are commonly used in the plastics, rubber, and food industries for processing materials like thermoplastics, elastomers, and dough-based products.
2. Conical Twin Screw Extruder

- As the name suggests, this type of twin-screw extruder features screws with a conical or tapered design.
- The screws have a larger diameter at the feed end and gradually decrease in diameter towards the discharge end.
- The conical design allows for better control over the pressure and shear forces experienced by the material during processing.
- Conical twin screw extruders are particularly useful for materials that require high shear rates or pressure buildup, such as in the production of highly filled or reinforced compounds.
- They are commonly employed in industries like plastics, rubber, and pharmaceuticals for processing materials with high viscosities or abrasive fillers.
The choice between a parallel or conical twin screw extruder depends on factors such as material properties, desired product characteristics, processing requirements, and production volumes. Manufacturers often collaborate with extruder suppliers to select the most suitable type and configuration for their specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and product quality.
Application of Twin Screw Extruder
Twin screw extruders are versatile machines that find applications across a wide range of industries, thanks to their ability to process diverse materials efficiently and produce high-quality extruded products. Let’s explore some of the key applications of twin screw extruders:
1. Plastics Industry
Twin screw extruders play a vital role in the plastics industry, where they are used for compounding, melting, and shaping various thermoplastic materials. They are employed in the production of pipes, profiles, sheets, films, cables, and other plastic products for applications in the construction, automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries. Plastic Twin screw extruders are also used in the processing of engineering plastics, filled and reinforced compounds, and masterbatches.
2. Rubber and Elastomer Processing
The high shear forces and efficient mixing capabilities of twin screw extruders make them suitable for processing rubber and elastomeric compounds. They are used in the production of rubber profiles, seals, gaskets, hoses, and other rubber-based products for the automotive, construction, and industrial sectors. Twin screw extruders are also employed in the compounding of rubber with additives, fillers, and reinforcements.
3. Food Industry
In the food industry, twin screw extruders are utilized for processing and texturizing various food products, such as snacks, cereals, pet food, and meat analogs. The high shear and temperature control capabilities of these machines allow for efficient cooking, gelatinization, and protein texturization processes. Twin screw extruders are also used in the production of ready-to-eat products, such as breakfast cereals and expanded snacks.
4. Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications
Twin screw extruders find applications in the pharmaceutical and biomedical industries for the production of drug delivery systems, such as sustained-release tablets and transdermal patches. They are used in hot-melt extrusion processes, where active pharmaceutical ingredients are combined with polymers to create controlled-release formulations.
5. Recycling and Reprocessing
Twin screw extruders contribute to sustainable practices by enabling the recycling and reprocessing of plastic waste and other materials. They are used to convert post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste into usable pellets or compounds, reducing environmental impact and promoting circular economy initiatives.
With their versatility, efficiency, and ability to handle a wide range of materials, twin screw extruders continue to be indispensable in various manufacturing processes, driving innovation and enabling the production of high-quality extruded products across diverse industries.
Final Thought
The twin screw extruder is a remarkable piece of machinery that has revolutionized manufacturing processes across numerous industries. From plastics and rubber to food and pharmaceuticals, these versatile machines have proven their worth through their excellent mixing capabilities, high output rates, and ability to handle a diverse range of materials.
Whether you’re looking to produce high-quality extruded products, compound materials with additives and fillers, or explore sustainable recycling and reprocessing solutions, a twin screw extruder can be the key to unlocking new possibilities for your business.
Visit our website if you want to learn more about Twin Screw Extruders. We also offer Single Screw Extruder for your comprehensive solution. If you looking for a Twin/Single Screw Extruder machine and need a guide to choose a suitable instrument for your specific need, please contact us now.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
2. How can a twin screw extruder improve our product quality and consistency?
The intermeshing screw design of a twin screw extruder creates high shear forces, ensuring that additives, fillers, and different polymers are blended thoroughly and evenly. The system also allows for precise temperature control along the barrel, which is crucial for preventing thermal degradation of sensitive materials. This level of process control results in a reliably consistent and high-quality final product, which is why companies rely on the robust engineering found in Torontech's twin screw extruders.
3. Our process involves challenging materials. Is a twin screw extruder a suitable choice?
Absolutely. Twin screw extruders are highly versatile and excel at processing materials that are difficult for single screw systems, including highly viscous polymers, abrasive compounds, and heat-sensitive materials. For especially demanding jobs like processing PVC powder or highly-filled compounds, specialized models are available. Consulting with an expert supplier like Torontech can help you select the optimal screw configuration for your specific material challenges.
4. How can a twin screw extruder support our company’s sustainability and recycling goals?
Twin screw extruders are ideal for recycling applications because their excellent mixing capabilities can effectively homogenize mixed or contaminated plastic waste. They incorporate venting zones that efficiently remove moisture and other volatiles, which is essential for processing post-consumer waste. By turning plastic waste into high-quality reusable pellets, a twin screw extruder from a knowledgeable provider like Torontech can be a cornerstone of a successful circular economy initiative.
5. What is the potential ROI when investing in a twin screw extruder?
The return on investment for a twin screw extruder is driven by several factors, including higher throughput, improved product quality, and reduced scrap rates. Their efficiency can also lead to lower energy consumption compared to other systems, especially in long-term operations. While the initial investment is higher than for a single screw machine, the increased productivity and flexibility often result in a faster ROI, a calculation that the team at Torontech can help you analyze for your specific production scenario.








