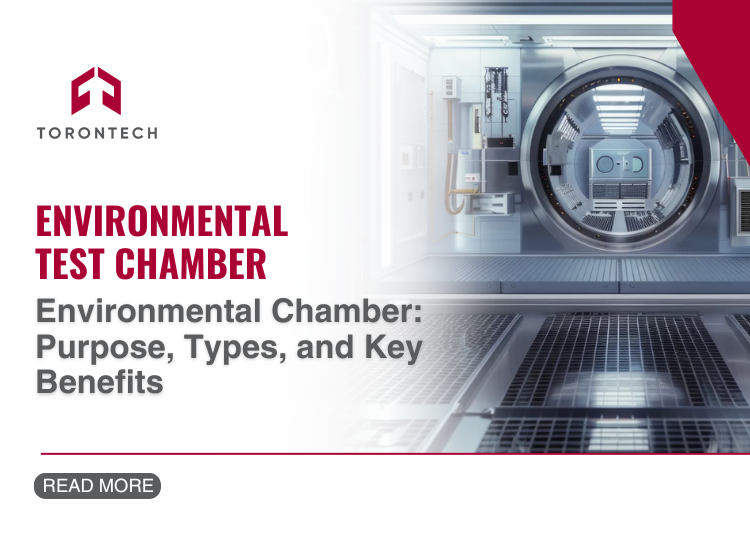
Products are often exposed to unpredictable environments during their lifecycle. From extreme heat to freezing cold, these conditions can affect performance and reliability. Environmental chambers help you identify potential weaknesses early, offering a controlled way to simulate harsh environments and ensure your products are ready for the challenges they might face.
If you’ve ever wondered how products are tested to withstand real-world challenges, this chambers hold the answer. This article will break down their functionality, types, and applications, helping you make informed decisions about testing equipment.
What Is an Environmental Chamber?

An environmental chamber, also called a climatic test chamber or testing chamber, is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment. It simulates various environmental conditions within a controlled space, allowing you to test how materials, products, or prototypes respond to these conditions. From extreme temperatures to high humidity or light exposure, these chambers can recreate scenarios your product might face throughout its lifecycle.
Environmental chambers are widely used to ensure product reliability and performance. Testing in these chambers provides valuable data on shelf life, operational limits, and potential weaknesses. This makes them an indispensable tool across industries such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, electronics, automotive, manufacturing, and more.
These chambers are still expensive today, but research is making significant advancements. For example, a low-cost environmental chamber designed specifically for warm climates uses readily available components, offering an affordable solution for testing applications in industries like agriculture and food science (Jing et al., 2023).
Some of the key environmental factors these chambers simulate include:
- Temperature variations (extreme heat or freezing cold)
- Humidity control
- Light dosage for photostability testing
- Cryogenic conditions for ultra-low temperatures
- And more.
These chambers help you make informed decisions during product development, reducing the risk of defects and costly recalls while enhancing overall quality.
How Does an Environmental Chamber Work?

Environmental chambers operate by simulating specific environmental conditions in a controlled and repeatable manner. These chambers are equipped with advanced components to maintain precise control over temperature, humidity, and other variables, ensuring reliable test results.
Here’s a closer look at how they work:
1. Temperature Control
The chamber’s cooling and heating systems work together to maintain the desired temperature. Cooling is achieved through a refrigeration system that uses a compressor, condenser, and evaporator to circulate refrigerant gas. Heating, on the other hand, relies on electric heating elements combined with a ventilation system to evenly distribute warm air.
2. Humidity Control
To simulate humid or dry conditions, the chamber uses two key mechanisms: humidification and dehumidification. An electric humidifier introduces moisture into the chamber in the form of steam, ensuring uniform humidity levels. Dehumidification relies on a cooling system, where moisture condenses on cold surfaces, reducing humidity in the chamber.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Modern environmental chambers come equipped with programmable control systems. These systems allow you to set test parameters, monitor conditions, and collect data in real-time. Interfaces often include touchscreens or computer software for seamless operation. Data transfer options like USB ports ensure you can easily analyze results externally.
Also, Innovative chambers now feature optical proxy measurement systems that provide real-time data on material phase changes, offering precise and high-throughput testing capabilities (Lyon et al., 2023).
4. Versatility Across Tests
Whether you’re simulating rapid temperature shifts (HALT/HASS testing) or exposing products to long-term humidity, environmental chambers provide unmatched flexibility. Some chambers also integrate additional capabilities like vibration, altitude simulation, or light exposure for specific testing needs.
Understanding how these chambers function gives you insight into their critical role in product testing. With this knowledge, you’ll be better prepared to explore their applications in the next section.
Applications of Environmental Chambers

Environmental chambers are versatile tools used across various industries to simulate and study the effects of environmental conditions on products and materials. Let’s explore some of the key applications:
1. Product Testing and Development
- Electronics: Environmental chambers test the durability of electronic components under extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibration. This ensures devices can withstand shipping, storage, and daily use across different climates.
- Automotive: Automotive manufacturers use these chambers to evaluate the performance of parts, tires, and electronics in hot, cold, and humid conditions, ensuring reliability and safety.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, chambers simulate harsh space conditions -extreme temperature fluctuations, vacuum, and radiation exposure- ensuring components can withstand space travel.
- Pharmaceuticals: Conducting stability testing on drugs and medical devices helps determine shelf life and ensures efficacy and safety under various storage conditions.
- Consumer Goods: From electronics to toys, consumer products undergo rigorous testing for durability and performance under diverse environmental stresses.
2. Research and Development
- Materials Science: Scientists study how temperature, humidity, and other factors affect the properties of metals, plastics, and composites, driving innovation in material design.
- Life Sciences: Researchers simulate natural conditions to study the growth and behavior of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Food Science: Environmental chambers are used to evaluate the shelf life, quality, and packaging integrity of food products during storage and transportation.
For research application, open-source environmental chambers have enabled cost-effective, high-precision studies on material stability, such as halide-perovskites, advancing material innovations in the energy and electronics sectors (Lyon et al., 2023).
3. Quality Control
- Manufacturing: Before hitting the market, products are subjected to environmental testing to ensure they meet quality standards, reducing the risk of defects and recalls.
- Military: Testing equipment for durability in extreme conditions -high altitudes, desert heat, and arctic cold- is critical for mission success.
Types of Environmental Chambers
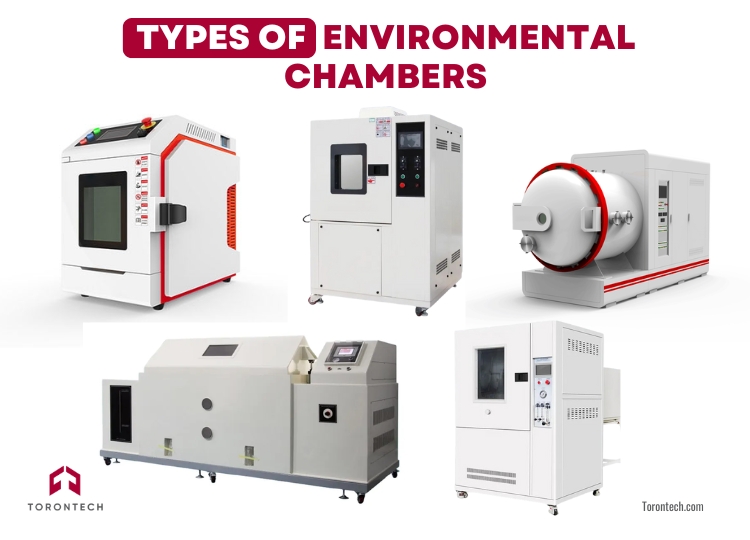

Environmental chambers come in various designs, each tailored to meet specific testing needs. Understanding the available types helps you choose the right one for your application.
1. Temperature and Humidity Test Chambers
These chambers are the most versatile and commonly used. They simulate a wide range of temperature and humidity conditions to test product durability and functionality. Ideal for electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive parts testing.
2. Thermal Shock Test Chambers
Designed to expose products to rapid temperature changes, these chambers have two or three zones (hot and cold). They are crucial for testing material resilience and identifying vulnerabilities in industries like aerospace and electronics.
3. Salt Spray Corrosion Test Chambers
Salt spray chambers simulate marine environments to evaluate corrosion resistance. Widely used in automotive, construction, and marine industries to test coatings, metals, and finishes.
4. Accelerated Weathering Test Chambers
These chambers replicate extreme weather conditions such as UV radiation, rain, and temperature fluctuations. They help predict how materials and products will age over time, making them essential for outdoor products and coatings.
5. Ozone Test Chambers
Ozone chambers evaluate the resistance of materials like rubber to ozone exposure. This is particularly important for industries such as automotive and medical device manufacturing.
6. Walk-In Environmental Chambers
Walk-in chambers offer large testing spaces for oversized products or bulk testing. These chambers are often used for automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment testing under complex environmental conditions. This type often used for building envelope testing, can accurately measure thermal performance (R-value) even under extreme conditions, such as −16 °C or 65 °C, with high precision (Zhang & Xu., 2023).
7. Vacuum Chambers
Vacuum chambers simulate high-altitude or space environments, testing products for aerospace and defense applications. They replicate vacuum conditions, extreme temperatures, and pressure changes.
8. Highly Accelerated Stress Test (HAST) Chambers
HAST chambers are used for accelerated reliability testing, exposing products to high heat and humidity. They are critical for electronics and semiconductor industries to ensure long-term reliability.
9. Dust and Rain Test Chambers
These chambers simulate dust, sand, and water conditions, testing product durability for outdoor and industrial applications. Common in automotive and military sectors.
10. Benchtop Environmental Chambers
Compact and cost-effective, benchtop chambers are designed for smaller-scale testing. They are ideal for laboratories and R&D departments with limited space.
Each type of environmental chamber is designed to address specific challenges. Selecting the right chamber depends on your testing requirements, the standards you need to meet, and the conditions your product will encounter in the real world.
Choosing the Right Environmental Chamber

Selecting the right environmental chamber can seem overwhelming with so many options available. By focusing on your specific needs, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your testing goals and ensures reliable results.
1. Define Your Testing Requirements
Start by identifying the environmental conditions your product will face. Are you testing for temperature, humidity, vibration, or other factors? Consider the following:
- Temperature Range: What is the minimum and maximum temperature required?
- Humidity Control: Do you need precise humidity levels for your tests?
- Special Conditions: Will you need to simulate vacuum, ozone, or salt spray?
2. Consider the Size and Capacity
The size of the chamber should match your sample size and testing volume.
- Benchtop Chambers: Suitable for smaller samples and limited space.
- Walk-In Chambers: Ideal for large or bulk testing, such as automotive or aerospace parts.
3. Look for Compliance with Standards
Ensure the chamber complies with relevant industry standards like ASTM, ISO, or MIL-STD. Compliance guarantees that your test results meet regulatory and quality requirements.
4. Evaluate Data Collection and Controls
Modern chambers offer advanced features for better control and data analysis. Look for:
- Programmable Controls: Easily set and monitor test parameters.
- Data Export Options: USB or Ethernet ports for transferring test data.
- Automation: Features like preset testing cycles to save time.
5. Assess Energy Efficiency and Maintenance
Energy-efficient chambers reduce operating costs over time. Consider models with features like:
- Insulated designs for better energy conservation.
- Low-maintenance components to reduce downtime and repair expenses.
6. Budget and Long-Term Investment
Price is an important factor, but remember to balance upfront costs with long-term reliability and functionality. A high-quality chamber can save money by minimizing maintenance and ensuring consistent performance.
7. Partner with a Trusted Supplier
Choose a supplier with a strong reputation for quality and support. Torontech, for instance, offers a wide range of environmental chambers backed by expert guidance, ensuring you find the perfect match for your needs.
Selecting the right chamber is key to improving product quality and ensuring performance under challenging conditions. With the right tools, you can simulate real-world environments and make confident, data-driven decisions.
Final Thoughts
Environmental chambers play a crucial role in ensuring product reliability and performance across various industries. From simulating extreme conditions to conducting long-term durability tests, these chambers provide invaluable insights that help manufacturers refine designs, enhance quality, and prevent costly defects.
Choosing the right type of these chambers depends on your specific needs, such as the type of testing, required environmental conditions, and compliance with industry standards.
Torontech offers a diverse range of advanced environmental chambers tailored to meet the demands of modern testing. With customizable options, precise control systems, and compliance with international standards.
References
- Jing, H., Zhao, X., & Wu, Q. (2023). A Low-Cost Environmental Chamber to Simulate Warm Climatic Conditions. Agricultural and Environmental Letters, 7(1), 24-30. https://doi.org/10.2134/ael2023.02.0023
- Lyon, S., Greenfield, J., & Turner, K. (2021). Accelerated Weathering Test Chambers: Applications and Developments. Materials Performance, 60(3), 40-45.
- Zhang, Y., & Xu, L. (2023). Innovative Environmental Chamber Construction for Accurate Thermal Performance Testing. Buildings, 13(5), 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13051259